
For example, in the absence of oxygen, E. Functions įacultative anaerobes are able to grow in both the presence and absence of oxygen due to the expression of both aerobic and anaerobic respiratory chains using either oxygen or an alternative electron acceptor. It has also been observed that these oxygen-sensitive proteins are protected within the cytoplasm by oxygen consumers within the cell membrane, known as terminal oxidases. Activities of these two regulators are indicative of spatial effects that may affect gene expression in the microaerobic range. There may exist a core network of transcription factors (TFs) that includes the major oxygen-responsive ArcA and FNR control the adaptation of Escherichia coli to changes in oxygen availability. coli K-12 in relation to the mechanism of the Pasteur effect. Given PFK’s role in glycolysis, this has implications for the effect of oxygen on the glucose metabolism of E. Additionally, in Escherichia coli K-12 it has been noted that phosphofructokinase (PFK) exists as a dimer under aerobic conditions and as a tetramer under anaerobic conditions. This indicates that topoisomerase I and its associated relaxation of chromosomal DNA is required for transcription of genes required for aerobic growth, while the opposite is true for DNA gyrase. The obligate aerobes were later found to have a defective DNA gyrase subunit A gene ( gyrA), while obligate anaerobes were defective in topoisomerase I ( topI). It has been observed that in mutants of Salmonella typhimurium that underwent mutations to be either obligate aerobes or anaerobes, there were varying levels of chromatin-remodeling proteins. Certain eukaryotes are also facultative anaerobes, including fungi such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae and many aquatic invertebrates such as nereid polychaetes. Some examples of facultatively anaerobic bacteria are Staphylococcus spp., Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Listeria spp., Shewanella oneidensis and Yersinia pestis. They can be found evenly spread throughout the test tube.Ī facultative anaerobic organism is an organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but is capable of switching to fermentation if oxygen is absent.

Unlike obligate anaerobes, they are not poisoned by oxygen. They gather in the upper part of the test tube but not the very top.ĥ: Aerotolerant anaerobes do not require oxygen as they use fermentation to make ATP. However, they are poisoned by high concentrations of oxygen. They gather mostly at the top because aerobic respiration generates more ATP than fermentation.Ĥ: Microaerophiles need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. They gather at the top of the tube where the oxygen concentration is highest.Ģ: Obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen, so they gather at the bottom of the tube where the oxygen concentration is lowest.ģ: Facultative anaerobes can grow with or without oxygen because they can metabolise energy aerobically or anaerobically.
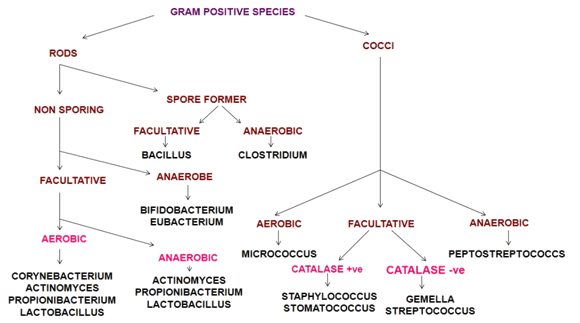
Aerobic and anaerobic bacteria can be identified by growing them in test tubes of thioglycolate broth:ġ: Obligate aerobes need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
